This is definitely a billion (or millions of) dollar(s) question. Anyone even remotely familiar with 5G will know that one of the use cases for 5G is mMTC or massive 'Machine Type Communications' (MTC - 3GPP defined name for M2M). We also looked at, not so long back, that even though it was predicted that there would be 50 billion cellular IoT devices by 2020, the total number is far behind.
In another recent post we argued that the IoT traffic will be shifting from 2G to 4G over the next few years because of the uncertainty of 2G networks in many countries after 2030. This has led to many IoT devices manufacturers to start thinking about not just 4G but also 5G.
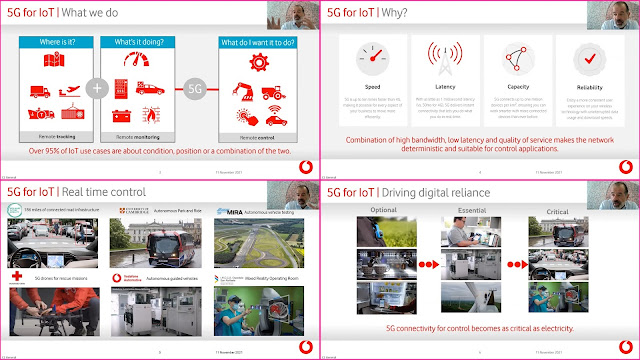
At the Telecoms Europe 5G conference back in November 2021, Erik Brenneis, CEO of Vodafone IoT presented their vision on how IoT is already mainstream and how IoT will make 5G mainstream. Here is the summary of his talk:
5G promises to be 10x faster than current LTE networks. This increase in speed will allow IoT devices to communicate and share data faster than ever. IoT connected devices are set to increase from 700 million to 3.2 billion by 2023. 5G is the most important facilitator for this revolution.
The video of his talk is embedded below:
A recently published post by Erik on Enterprise IoT Insights, 'Five trends that will shape the next decade in IoT' is also worth reading.
There are some major shifts ahead of the IoT sector. Our director, Erik Brenneis shares 5 leading trends in his article: 👉 https://t.co/uZaAk68irF #NBIoT #LPWA #5G #IoT
— Vodafone IoT (@VodafoneIoT) January 21, 2022
Related Posts:
- The 3G4G Blog: Are there 50 Billion IoT Devices yet?
- Connectivity Technology Blog: Will Amazon Sidewalk accelerate IoT Adoption?
- Connectivity Technology Blog: The Wide Variety of Internet of Things (IoT) Technologies for Different Situations
- Connectivity Technology Blog: The Potential of Connectivity Technologies Already Available Today
- Connectivity Technology Blog: Is 4G the new 2G in IoT?
- Connectivity Technology Blog: Cellular Connectivity Technology Landscape and Standards for Industrial IoT
- Connectivity Technology Blog: Helium - Another IoT Kid on the Block
- Connectivity Technology Blog: LoRa is quietly marching on...
- 3G4G: Internet of Things (IoT) and Machine-2-Machine (M2M)
Comments
Post a Comment